A massive underwater volcano located approximately 300 miles off the coast of Oregon is on the verge of erupting, scientists say, and for the first time, the public can witness it live.
Chadwick described Axial Seamount’s behavior as similar to volcanoes in Hawaii, characterized by the gradual buildup of pressure between eruptions.
If an eruption does occur, it is expected to release over a billion cubic feet of highly fluid lava, which scientists estimate would weigh millions of tons.
No Threat to Humans, but a Breakthrough for Science Despite its immense scale, an eruption from Axial Seamount poses no threat to coastal communities.
Experts emphasize that its location far offshore and deep beneath the ocean renders it harmless to humans and without consequence for land-based seismic activity.
Scientists say a huge underwater volcano about 300 miles off the coast of Oregon is about to erupt, and the public will be able to see it firsthand for the first time. Oregon State University researchers have been keeping a careful eye on the location, which is located on the Juan de Fuca Ridge, a geologically active area off the Pacific Northwest. Comparable to a balloon filling up before it bursts, the volcano is thought to be the most active in the region, and data shows that its magma chamber is rapidly expanding.
Warning Indications Reflect the 2015 Explosion.
Almost 8,000 underwater earthquakes were caused by the 2015 eruption of Axial Seamount, which also released lava flows that were hundreds of feet thick and caused the seafloor to collapse by roughly eight feet. Thanks to a variety of new tools, such as pressure sensors and high-definition video cameras set up through the Ocean Observations Initiative, that event signaled a paradigm shift in how scientists monitor underwater volcanic activity.
Oregon State University geophysicist and volcanologist William Chadwick stated that the volcano is currently “at or almost at that inflation threshold” seen before the 2015 eruption. “We believe it is ready,” he continued. According to sensor and satellite data, the seafloor above Axial has swelled to almost the same size as it was right before that last eruption.
An uncommon look at volcanic activity in the deep sea.
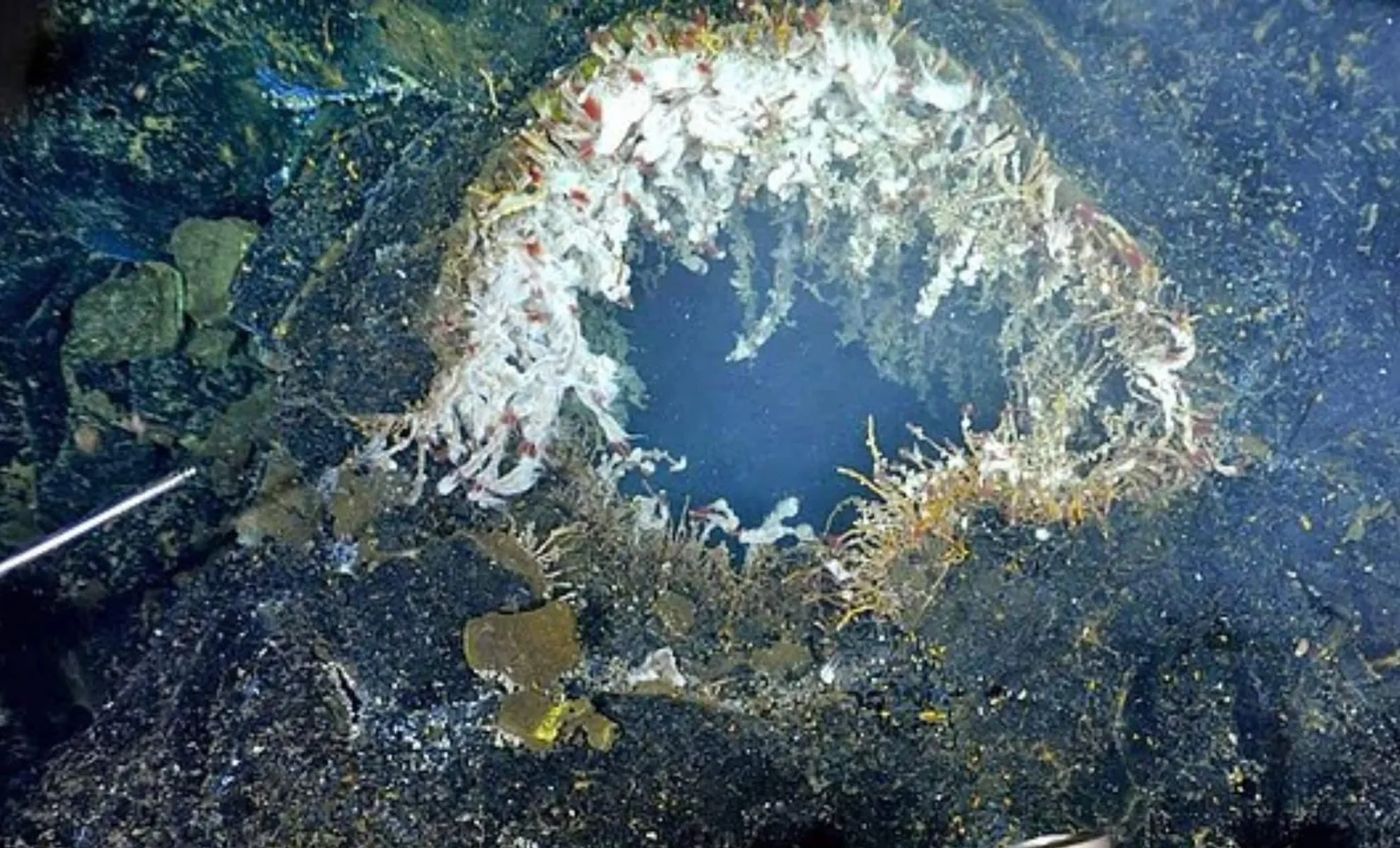
Scientists have placed a live camera feed close to the volcano’s summit to record the events as they happen, and the Interactive Oceans website will stream livestreams every day. The main subject of the video is “Mushroom,” a 14-foot-tall hydrothermal formation in the ASHES vent field on the western flank of Axial.
Tube worms and white bacterial mats, which are obvious indicators of hydrothermal activity and warm fluids leaking through the basalt fissures, surround this vent, which is situated atop an old lava flow.
Chadwick explained that the behavior of the Axial Seamount is comparable to that of Hawaiian volcanoes, which are distinguished by the slow accumulation of pressure in between eruptions. He clarified that “they tend to inflate like a balloon in between eruptions.”. The seafloor is truly rising at Axial, which is a strong indication. “.”.
Growing pressure is indicated by increased seismic activity.
Seismic activity beneath the volcano has significantly increased in recent weeks, indicating that magma is pressing upward with greater intensity. Within 24 hours of the eruption starting, the number of underwater earthquakes, which are currently occurring at a rate of several hundred per day, is predicted to increase to as many as 10,000.
When the rate of seafloor swelling started to pick up speed again after stagnating for a few years, Chadwick and his team became aware of these changes for the first time in November 2024. Rapid changes in the volcano’s shape and internal pressure dynamics were indicative of its “sudden waking up,” according to a 2024 study.
Scientists estimate that over a billion cubic feet of extremely fluid lava, weighing millions of tons, would be released if an eruption did occur. Lava flows may rise to heights similar to the Space Needle in Seattle.
It’s a scientific breakthrough, but not a threat to people.
Coastal communities are not in danger from an eruption from Axial Seamount, despite its enormous size. Experts stress that because it is located far offshore and deep under the ocean, it poses no threat to people and has no bearing on seismic activity on land.